Introduction
In the realm of messaging systems and message brokers, protocols like MQTT, AMQP, and STOMP often reign supreme. These protocols are well-suited for asynchronous communication and are the go-to choice for many messaging scenarios. However, there are instances where you might want to employ a different approach, such as using HTTP, to achieve specific automation goals. In this blog post, we’ll explore the advantages of using HTTP for automation, especially when integrating with RabbitMQ, and how tools like Automation for Jira can facilitate this process.
Messaging Protocols
Messaging systems typically rely on messaging protocols to facilitate communication between producers and consumers. These protocols ensure that messages are delivered reliably and efficiently, making them the backbone of many messaging solutions. They are particularly well-suited for scenarios where real-time communication and message queuing are essential.
HTTP
While messaging protocols are fantastic for many use cases, there are scenarios where using HTTP can be more advantageous. HTTP is a stateless, text-based protocol commonly associated with web communication. Here’s why it can be an excellent choice for automation:
- Simplicity: HTTP requests are easy to understand and work with. They involve standard methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, making them accessible to a wide range of developers.
- Compatibility: Almost every modern system and programming language supports HTTP, making it a universal choice for integration.
- Automation Tools: Many automation tools, like Automation for Jira, are designed to work with HTTP endpoints, enabling seamless integration with a variety of services, including message brokers like RabbitMQ.
CloudAMQP Console
CloudAMQP is a cloud-based RabbitMQ service that simplifies message queueing for developers and project managers. The CloudAMQP Console serves as a central hub for managing your RabbitMQ instances and exchanges. To get started, visit cloudamqp.com and create an account if you don’t already have one.
RabbitMQ Management (cloudamqp.com)
RabbitMQ is a robust message broker that plays a pivotal role in message queuing and routing. With CloudAMQP, you can easily manage RabbitMQ instances, exchanges, queues, and more. Let’s delve into some key concepts:
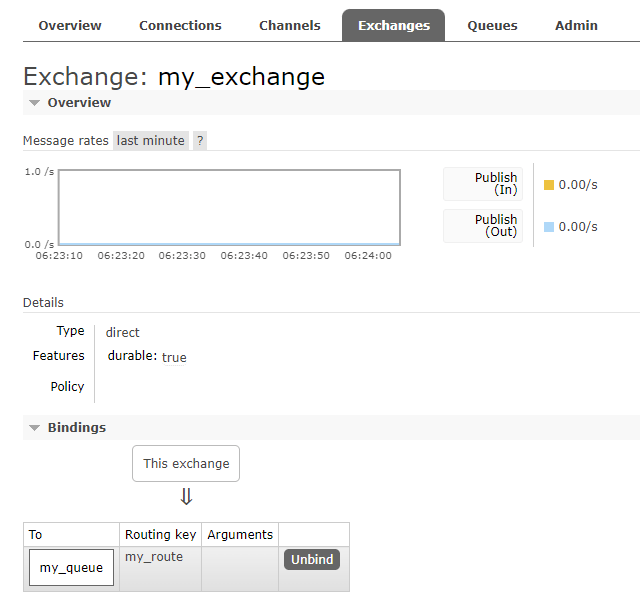
Exchange
An exchange in RabbitMQ is responsible for routing messages to the correct queue(s). It acts as a mediator that receives messages from producers and routes them to one or more queues based on rules defined by the exchange type.
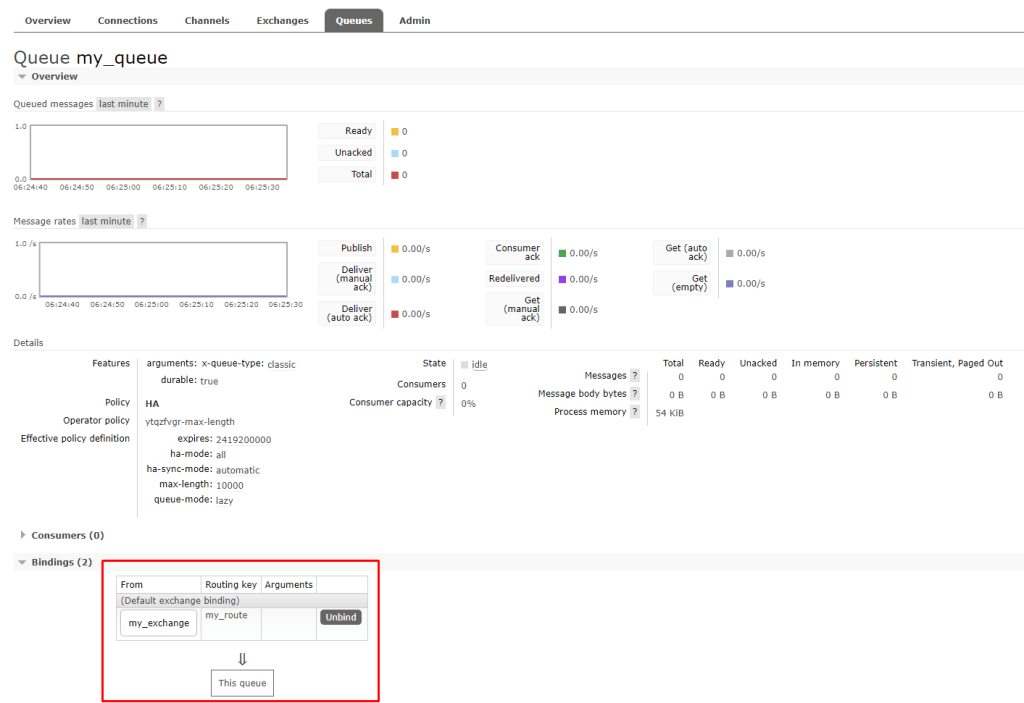
Queue
A queue is a storage location where messages are held until they are consumed by a consumer. Queues are essential for managing and distributing messages efficiently.
Request
Now, let’s see how you can use the CloudAMQP Console in conjunction with RabbitMQ to send a message to an exchange:
https://<user>:<password>@toad.rmq.cloudamqp.com/api/exchanges/<user>/<exchange>/publish/
{"properties":{},"routing_key":"my_route","payload":"Hello, world!","payload_encoding":"string"}
In this example, replace <user>, <password>, and <exchange> with your specific CloudAMQP credentials and exchange name. This request will publish a message with the text “Hello, world!” to the specified exchange with the routing key “my_route.”
Response
Upon successfully sending the request, you will receive a response like the one below:
{
"routed": true
}
This response indicates that the message was successfully routed to the specified exchange.
Conclusion
While traditional messaging protocols are invaluable for many messaging scenarios, HTTP offers a different avenue, especially when automation is a primary goal. Using HTTP, you can integrate messaging systems like RabbitMQ with automation tools like Automation for Jira seamlessly.
So, whether you’re looking to automate message publishing, create custom workflows, consider the versatility of HTTP and its compatibility with automation tools as part of your toolkit.
