Introduction
Fostering a culture of innovation is paramount to staying ahead. This post sheds light on a successful implementation of Jira for Idea Management, designed to promote engagement and participation among employees. This initiative has not only stimulated organizational creativity but also contributed significantly to positive changes and accomplishments within one of the world’s leading companies in agribusiness, food, and ingredients.
As one of the first projects I encountered in my Atlassian consulting journey back in 2013, this endeavor proved to be a sensational example of effective functionality. Generating millions in economic value and improvements for the global agribusiness giant.
The project was implemented in 2007, but it is still very valid and current.
How it was Implemented
The innovation project unfolded in three distinctive waves, each marking a crucial phase in the evolution of the organizational processes and culture:
🌊 First Wave: Idea Generation and Awareness
- Objective: The initial phase marked the beginning of the journey, focusing on generating and capturing ideas, raising awareness of the innovation process, and enhancing existing processes and products.
- Activities: Users actively participated in submitting ideas, creating a culture of awareness and improvement.
- Outcome: The organization witnessed a surge in idea generation, fostering a heightened consciousness of the innovation process, and initiating improvements in both processes and existing products.
🌊 Second Wave: Evaluation and Implementation
- Objective: The second wave shifted the focus to the evaluation and implementation of improvements, primarily led by the Project Office.
- Activities: Rigorous evaluation processes were implemented, and selected ideas moved through development and implementation phases.
- Outcome: The organization experienced tangible changes as selected ideas were successfully implemented, contributing to enhanced products and services.
🌊 Third Wave: Business Incubation for New Ventures
- Objective: With processes well-established and running smoothly, the third wave aimed to create a business incubator for new products, services, markets, and ventures.
- Activities: Building on the successes of the first two waves, this phase involved creating an environment to nurture and incubate innovative business ideas.
- Outcome: The organization expanded its horizons, creating a platform for exploring and launching new products, services, and business opportunities.
This encapsulates a journey of innovation and growth, where each wave contributed to a cumulative and transformative experience, showcasing the organization’s commitment to continuous improvement and entrepreneurial exploration.
The Project’s Areas of Focus
📌 Idea Management Portal: The initial portal, known as the Idea Management, played a pivotal role in:
- Identifying Opportunities
- Mobilizing Internal and External Sources
- Generating and Capturing Ideas
- Evaluating, Selecting, and Prioritizing
- Developing Concepts
📌 Project Office: Following idea submission, the Project Office team took charge of:
- Project and Portfolio Management
- Partner Management
- Financing
- Monitoring Innovation Activities
Project Overview
The Jira Service Management project, named “Ideas & Innovation Management,” was created to empower employees to submit improvement ideas that could yield benefits for themselves, their departments, or the entire company.
The workflow of the Idea comprised the following statuses:
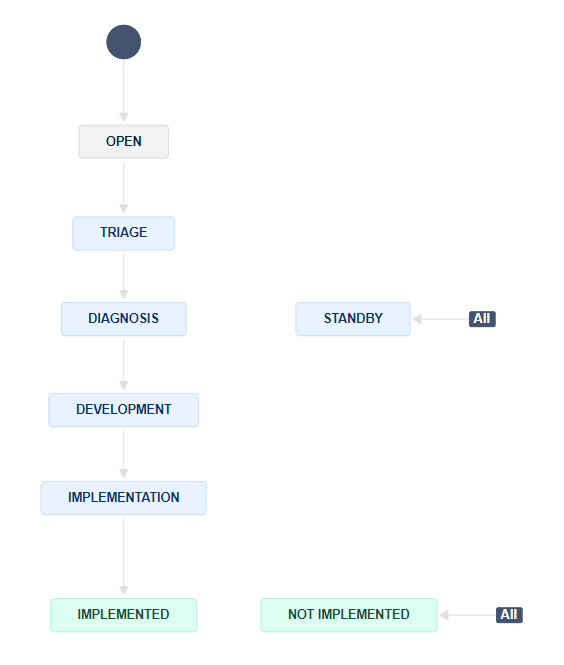
- Idea Registration (Open):
- Purpose: Users submit their innovative ideas for improvement or change.
- Activities: Submitters provide details such as the idea’s destination area, focus, objective, description, and any relevant attachments.
- Outcome: The idea is officially registered in the system for evaluation.
- Responsible: All employees
- Triage:
- Purpose: Initial assessment to categorize and prioritize ideas.
- Activities: Ideas are reviewed to determine their viability, relevance, and potential impact.
- Outcome: Ideas are categorized based on their feasibility and prioritized for further evaluation.
- Responsible: Innovation Team
- Diagnosis:
- Purpose: In-depth analysis of selected ideas.
- Activities: Detailed evaluation of the feasibility, benefits, and alignment with organizational goals.
- Outcome: Ideas are diagnosed to determine their potential for development and implementation.
- Responsible: Innovation Committee
- Standby:
- Purpose: Temporary hold for further considerations or resource planning.
- Activities: Ideas that require additional information or resources are put on standby.
- Outcome: Ideas await further clarification or resource availability.
- Responsible: Innovation Committee
- Development:
- Purpose: Actively working on transforming approved ideas into actionable plans.
- Activities: Planning, designing, and creating strategies for implementing the selected ideas.
- Outcome: Development phase focuses on turning ideas into tangible project plans.
- Responsible: Innovation Committee
- Implementation:
- Purpose: Putting the planned strategies into action.
- Activities: Executing the developed plans, deploying resources, and monitoring progress.
- Outcome: Ideas are actively implemented in the organization to bring about positive change.
- Responsible: Innovation Committee
- Not Implemented:
- Purpose: Closure for ideas deemed unfeasible or not aligned with organizational goals.
- Activities: Communicating reasons for non-implementation to submitters.
- Outcome: Ideas that do not meet the criteria for implementation are officially closed, providing closure for submitters and the organization.
- Responsible: Innovation Committee
User-Friendly Idea Submission
The simplicity of idea submission was a key focus. The fields for creating an idea included:
Destination Area / Committee ⚗️

This area refers to the specific domain or department within the organization to which the idea is directed. Once an idea is submitted, it undergoes evaluation and approval by dedicated committees associated with the respective destination areas.
The committees are entrusted with the responsibility of thoroughly assessing each idea. Their role involves evaluating the feasibility, impact, and alignment of the proposed innovation with the goals and objectives of the designated area. Committees play a pivotal role in the decision-making process, providing valuable insights and expertise to determine whether an idea should proceed to the next stage.
Idea Focus 🔬
When submitting an idea, individuals are often asked to specify the primary area or aspect that the idea is intended to address or improve. This helps in organizing and categorizing ideas based on their main objectives or purposes.
For example, if the idea pertains to streamlining communication processes within a specific department, the “Idea Focus” could be “Communication Efficiency” or “Internal Collaboration.” This categorization aids in better understanding and organizing a diverse range of ideas, making it easier for decision-makers and evaluators to identify patterns, prioritize initiatives, and align ideas with strategic goals.
Many times the company wanted to focus on specific ideas for a particular problem. To achieve this, the company conducted campaigns for the employees, so they would choose a specific item from this list that pertained to this challenge.
Objective 🎯
The Objective refers to the specific goal or purpose that the submitter aims to achieve by proposing the idea. When submitting an idea, individuals are often asked to articulate the overarching intention or desired outcome of their proposed innovation. It helps evaluators, decision-makers, and other stakeholders understand the strategic intent behind the idea, making it an essential component of the idea description.
Description 📃
Refers to a detailed explanation or narrative that provides comprehensive information about the proposed idea. It is a crucial element as it allows the submitter to articulate the idea’s concept, rationale, potential benefits, and any other relevant details that can help others understand the idea in depth.
Attachments 📪
Refer to additional files, documents, images, or any supplementary materials that the submitter can include along with their idea.
Metrics for Success
To measure the success of the project, various metrics were established, including:
- Revenue and Savings from Innovation Projects
- % Contribution of New Products
- Quantity of Evaluated Ideas
- Quantity of Implemented Ideas
- Ideas Generating Financial Returns
- Time to Market (days)
- Financial Return (in U$)
- Total Points Earned
Rewarding and Incentive 🎉
- Points and Rewards: users who submitted ideas earned points at each approval or stage completion. These points could then be exchanged for exciting prizes, such as devices, swag items, TVs, or any other rewards defined by the company.
- Another process in Jira was designed for users to request the prize they desired based on the points they had accumulated. Therefore, they had two options: continue earning points to exchange for something greater or redeem the points to claim the prize they had chosen.
- Innovation Award: The top three ideas of the year were rewarded with an additional salary.
- Performance Award – Committees: Committees are assessed throughout the months, and the committee with the best performance at the end of the year is honored.
- Profit Sharing: Employees participate in the results.
- Publication in Internal Magazine and Corporate Portal: Ideas are featured in the internal magazine and corporate portal for wider recognition.
Conclusion🧠
The Ideas & Innovation Management project has proven to be a game-changer, not only in streamlining the idea generation process but also in creating a culture of innovation that is rewarded and celebrated. This successful implementation serves as a testament to the power of leveraging tools like Jira for fostering creativity and driving positive change within organizations.
There is no single MODEL for fostering innovations. There are PRACTICES that either promote or inhibit innovation: Workplace environment and company culture – encourage teamwork and cross-departmental collaboration, – foster an entrepreneurial spirit, and embrace errors as part of the learning process.
From a technical standpoint, this project was implemented in a Jira version 3 (can you imagine?). So, a lot of customization, configuration, and development was necessary. Today, a project like this, with all the standard functions available in Jira Service Management, could have been developed in days using Automation for Jira and other standard features.